
Initiation of a Production Line for Catalyst Materials for the Petrochemical and Automotive Industries
4 March 2025
No Comments
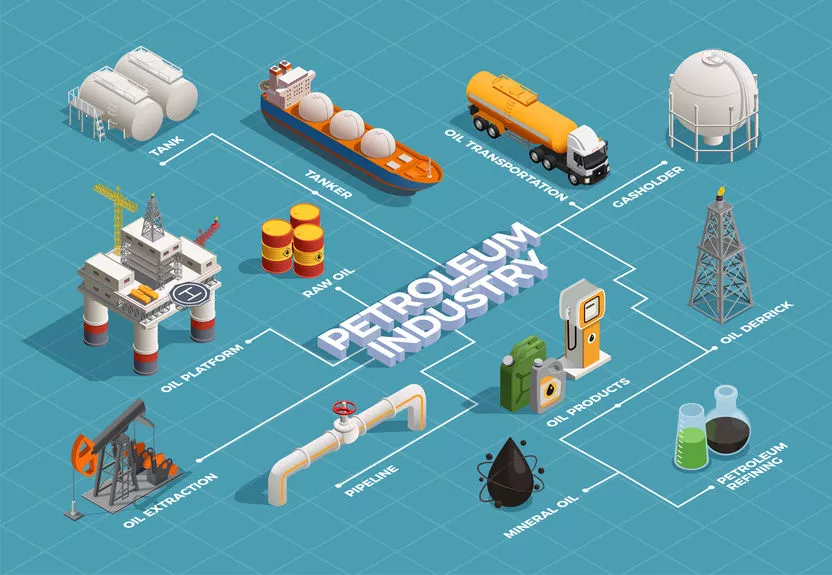
Crude oil is one of the most crucial energy sources and raw materials in the world. After refining, it is transformed into a wide range of derivatives used in transportation, energy production, chemical industries, and even everyday consumer products. This article explores the production processes, types of petroleum derivatives, and their role in various industries.
Petroleum derivatives are substances obtained from the refining of crude oil. These products are classified based on molecular weight and boiling points into three main categories:
This category includes low-boiling point materials such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), gasoline, and naphtha, which are primarily used as fuels and chemical feedstocks.
This group consists of diesel, jet fuel, and kerosene, which are commonly used in transportation and industrial applications.
Products like residual fuel oil, bitumen, asphalt, and industrial lubricants fall into this category. These are used in energy production, road construction, and manufacturing industries.
The primary step in oil refining, fractional distillation, involves heating crude oil in a distillation tower to separate it into different fractions based on their boiling points, such as gasoline, diesel, and fuel oil.
This process breaks down heavier molecules into lighter, more valuable fuels like gasoline and diesel through the use of heat and catalysts.
These processes enhance the octane rating of gasoline, improving its quality and efficiency.
A process that removes sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen compounds to improve the quality and environmental compatibility of petroleum products.
One of the most essential petroleum products, gasoline is used as a fuel for automobiles and internal combustion engines.
A primary fuel for diesel-powered vehicles, trucks, trains, and some industrial machinery.
These fuels are widely used in aviation and for heating purposes.
These products are primarily used for energy production in power plants and large industrial facilities.
Derived from the heavier fractions of crude oil, these materials are used in road construction, roofing, and waterproofing applications.
Used for cooking, heating, and as an alternative automotive fuel.
These products reduce friction and wear in industrial machinery and equipment.
Many plastic products are derived from petroleum-based compounds such as polyethylene and polypropylene.
Petroleum-based compounds are used as surfactants in detergents and various cosmetic products.
Ammonia and urea, derived from petroleum products, are widely used in agriculture.
Certain chemical solvents obtained from petroleum are essential for the production of paints, coatings, and industrial chemicals.
Fossil fuels contribute significantly to carbon dioxide emissions and climate change.
Oil spills and petroleum waste can lead to severe pollution of water bodies and land.
Proper recycling and disposal of petroleum waste remain a major environmental challenge.
Solar, wind, and hydroelectric energy can serve as substitutes for fossil fuels.
Bioethanol and biodiesel, derived from renewable resources, offer more sustainable energy solutions.
Innovative technologies are being developed to recycle petroleum-based waste into reusable products.
Petroleum derivatives play a vital role in the global economy and everyday life. From transportation to the chemical industry, human dependence on these resources is undeniable. However, environmental concerns and the depletion of fossil fuels have led to increased attention toward alternative energy sources and sustainable methods.
